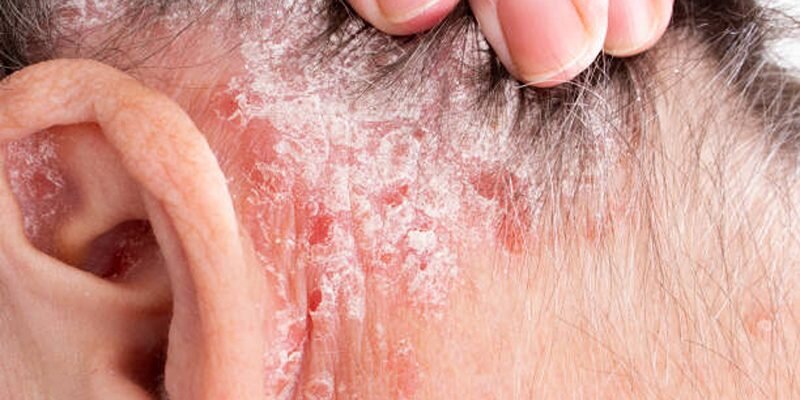
Understanding Ear Eczema: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Advertisement
Ear eczema, a common skin condition affecting the delicate skin of the ear, can be a source of discomfort and frustration for many individuals. Characterized by inflammation, itching, and redness, ear eczema can occur in the outer ear, the ear canal, or both. Multiple factors contribute to its development, including environmental influences, allergies, and genetic predisposition. Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to more effective management and treatment, preventing further complications. While the exact causes may vary from person to person, understanding the triggers is crucial in formulating a personalized approach to alleviate symptoms. Treatments range from topical creams and ointments to lifestyle adjustments aimed at avoiding irritants.
What is Ear Eczema?
Ear eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is more than just a skin conditionit's a frustrating and persistent battle with dryness, itchiness, and inflammation. When it strikes the ears, it can be especially troublesome, as the sensitive skin in and around our ears is easily irritated. Living with ear eczema can be uncomfortable, but understanding it is the first step toward finding relief!
There are different types of ear eczema, such as:
- Atopic eczema: The most common type, typically associated with other allergic conditions like asthma or hay fever.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: Causes flaky, oily skin, often seen in the scalp and behind the ears.
- Allergic contact dermatitis: Triggered by contact with allergens like certain metals, fragrances, or skincare products.
Symptoms of Ear Eczema:
The symptoms of ear eczema vary depending on the severity of the condition and the specific type of eczema. Some common signs to watch for include:
- Itching: One of the most common symptoms. It can be intense, leading to scratching, which may worsen the condition.
- Redness and inflammation: The skin around or inside the ear may become red and inflamed.
- Dry, flaky skin: The affected area may appear dry, scaly, or cracked.
- Clear fluid discharge: In severe cases, eczema can cause oozing or a clear fluid discharge from the ear canal.
- Swelling: The ear may swell, especially if the eczema becomes infected.
- Crusting: The skin can develop crusts or patches, often resulting from scratching or infection.
Causes of Ear Eczema:
Ear eczema has multiple potential triggers, and understanding these can help in managing the condition.
1. Genetics and Family History
If you have a family history of eczema, asthma, or other allergic conditions, you're more likely to develop ear eczema. The genetic predisposition may make the skin more sensitive to irritants.
2. Environmental Factors
External factors such as pollution, harsh weather, or dry air can irritate the skin, triggering eczema flare-ups. People who live in dry climates or are exposed to chemicals or pollutants may experience worsening symptoms.
3. Allergies
Certain allergens, such as nickel (found in earrings), cosmetics, shampoos, and even hearing aids, can cause allergic contact dermatitis. Identifying and avoiding these allergens can help reduce the risk of flare-ups.
4. Skin Irritation
Wearing headphones, earplugs, or using harsh cleaning agents on or around the ears can irritate the skin and lead to eczema. Excessive cleaning of the ear canal, especially with cotton swabs, can also damage the skin and cause irritation.
5. Infections
Bacterial or fungal infections can complicate eczema, making symptoms worse. Moist environments, like the inside of the ear, are particularly susceptible to infections, which can lead to additional inflammation and discomfort.
Diagnosing Ear Eczema:
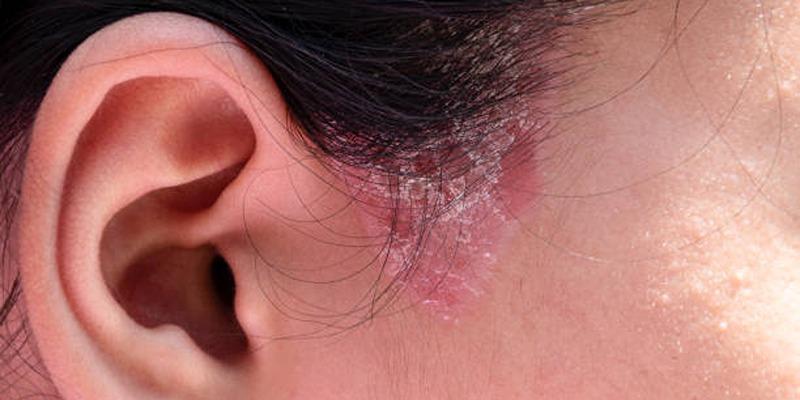
A dermatologist or healthcare provider can diagnose ear eczema by thoroughly examining the affected area, often looking for signs such as redness, itching, and flaking skin. In some cases, patch tests may be conducted to identify specific allergens, particularly if allergic contact dermatitis is suspected. These tests involve applying small amounts of various substances to the skin and monitoring for reactions.
Identifying the specific cause of the eczema is crucial, as it allows healthcare professionals to tailor the most effective treatment plan. This may include recommendations for topical medications, lifestyle changes, and avoidance of identified irritants or allergens to help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Treatment Options for Ear Eczema:
Treating ear eczema involves a combination of lifestyle changes, topical treatments, and, in some cases, medications. Here are the primary treatment options available:
1. Topical Steroids
For more severe cases of ear eczema, topical corticosteroids are often prescribed. These are applied directly to the affected area to reduce inflammation, itching, and redness. It is important to use these under a doctors supervision, as overuse can thin the skin.
2. Moisturizers and Emollients
Keeping the skin moisturized is essential in managing eczema. Using gentle, fragrance-free moisturizers helps to prevent dryness and flaking. Emollients like petroleum jelly or ointments can be used to lock in moisture and protect the skin.
3. Antibiotics or Antifungals
If the ear eczema becomes infected, your doctor may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics or antifungals to clear up the infection. Its crucial to treat infections promptly to prevent further complications.
4. Antihistamines
If itching is severe, antihistamines may be recommended to help control the urge to scratch and reduce allergic reactions.
5. Allergen Avoidance
For those with allergic contact dermatitis, identifying and avoiding the allergen is key. For example, switching to hypoallergenic earrings, fragrance-free skincare products, and avoiding known irritants can help prevent flare-ups.
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Ear Eczema:
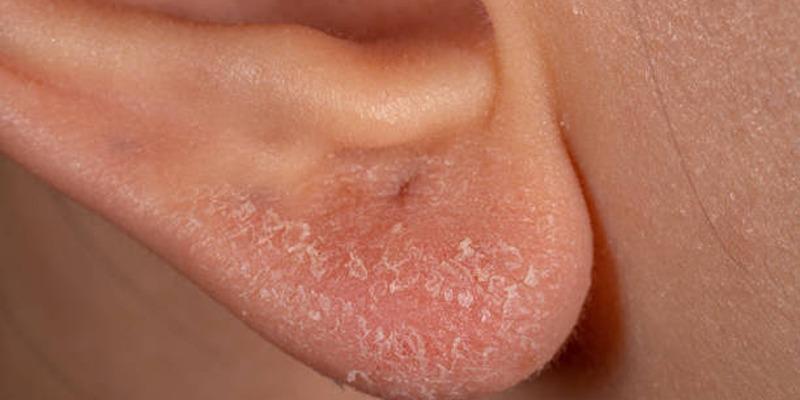
In addition to medical treatments, some lifestyle changes can help manage ear eczema and reduce flare-ups:
- Avoid irritants: Identify potential irritants, such as certain soaps, shampoos, and metals, and eliminate them from your daily routine.
- Wear soft, breathable fabrics: If eczema extends to the area behind the ears, wearing soft, non-irritating clothing can help.
- Use mild, fragrance-free products: Harsh soaps, detergents, and fragrances can trigger eczema. Stick to products designed for sensitive skin.
Conclusion:
Ear eczema is a manageable condition, but it can significantly impact daily life if left untreated. Understanding its symptoms and triggers is the first step toward effective management. With the right treatment plan, including topical treatments, lifestyle changes, and allergen avoidance, most people with ear eczema can control their symptoms and prevent flare-ups. If you experience any signs of infection or persistent discomfort, it's important to seek professional medical advice to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. By taking a proactive approach, you can minimize the impact of ear eczema on your overall well-being.
On this page
What is Ear Eczema? Symptoms of Ear Eczema: Causes of Ear Eczema: 1. Genetics and Family History 2. Environmental Factors 3. Allergies 4. Skin Irritation 5. Infections Diagnosing Ear Eczema: Treatment Options for Ear Eczema: 1. Topical Steroids 2. Moisturizers and Emollients 3. Antibiotics or Antifungals 4. Antihistamines 5. Allergen Avoidance Lifestyle Tips for Managing Ear Eczema: Conclusion:Advertisement