How Is Asthma Diagnosed: A Step-by-Step Guide to Understanding the Process
Advertisement
Do you have difficulty breathing or hear a wheezing sound when you breathe, along with cough and chest pain? If yes, then you should be alarmed because these can be the indications of asthma, which is often left undiagnosed and, hence, untreated. Untreated asthma can become complicated, so you must see a doctor quickly. Yes, effective treatments for asthma are available, including bronchodilators and anti-allergens.
However, all the medications only work when the disease is diagnosed promptly. The condition is usually diagnosed by physical examination and lung function tests, which include spirometry, peak flow meter tests, trigger tests, methacholine challenge tests, and allergy tests like skin prick tests and serum-specific IgE tests. If you are still interested in learning about asthma diagnoses in detail, let's learn about them together here!

What is Asthma: An Understanding
Asthma, or bronchial asthma, is a chronic condition that affects the lungs. It is common in both children and adults. An asthmatic patient experiences difficulty in breathing due to bronchospasm, inflammation, and mucus production. The muscles around the airways tighten, making the air passage narrow. The lining of these airways gets inflamed, which causes difficulty breathing. Mucus production also blocks the airways. All of this produces a wheezing sound when you breathe, which is the major symptom of asthma. Other symptoms include trouble sleeping, coughing, and chest pain. Asthma can be allergic or non-allergic.
As the name indicates, allergens trigger allergic asthma, while stress, weather changes, exercise, and other illnesses trigger non-allergic asthma. The condition usually develops during adulthood and lasts for a lifetime. Asthma usually goes away in children but can come back during the teenage years or even later in life. Although asthma can be controlled, it can lead to serious complications if left unattended. It can result in lethargy, anxiety, depression, lung infections like pneumonia, and delay in growth and puberty. Severe asthma attacks can be life-threatening.
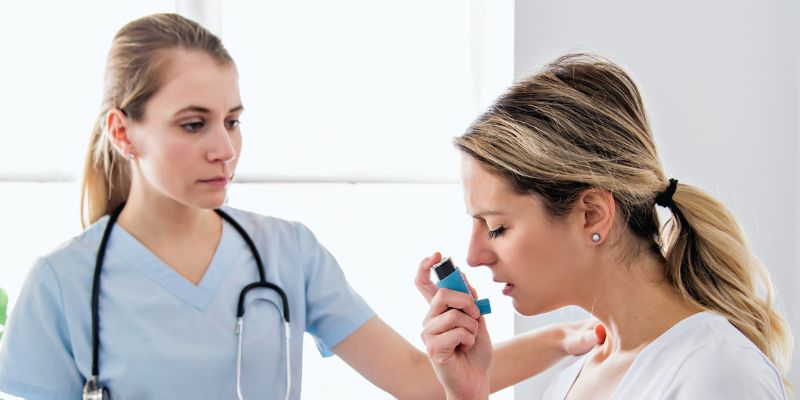

Diagnosis of Asthma: Understanding The Process
Are you experiencing some unusual symptoms like breathlessness, chest pain, and cough but don’t know why it is so? All of these could be the signs of asthma. So, you must consult a doctor and get yourself checked. Correct and timely diagnosis of the disease is crucial for properly treating it. To diagnose asthma, the doctor will take your medical history and perform some physical tests for confirmation. Lung function tests and many other important tests are used to diagnose asthma. Let’s learn all about the asthma diagnosis here:
Personal and Medical History
Taking personal and medical history includes asking questions about and understanding your symptoms so the doctor can conclude what you are going through. The common questions include:
- If there is any family history of asthma and allergies
- If you are taking any medication
- Your lifestyle and your symptoms
- If you have any other medical issues
People having a history of allergies or eczema are more likely to get asthma, and you should tell your doctor honestly about it. You should also notice and tell your doctor what triggers your symptoms, such as pet dander, dust, mites, mold, and pollen grains. The triggers can also be pollutants, chemicals, and smoke. Besides this, you must also inform your doctor if you get chest symptoms when you exercise, during sleep, using any specific medicine, or during weather changes.
Physical Examination
Personal and medical history will be insufficient to confirm whether you are suffering from asthma. Physical examination is also important. The physical examination for asthma includes examining the patient's eyes, ears, nose, throat, and skin. The doctor also listens to the lungs and chest. The oxygen level in your chest is also measured using a pulse oximeter. Sometimes, an X-ray of the lungs or sinuses is also needed.
Lungs Function Tests
The confirmation tests for asthma, known as lung function tests, are done to check breathing. These tests check how well you can inhale and exhale air in and out of your lungs. They also measure lung capacity and check for any blockage in your airways. These tests are performed before and after using the bronchodilator, the inhaling device used for asthma, to open the airways and improve lung functioning. The common types of lung function tests include the following:
- Spirometry: This test measures the level of air you breathe in and out and checks your breathing speed.
- Methacholine Challenge Test: The methacholine test uses methacholine medicine, which tightens the airways, which is intense in people with asthma. First, a spirometry measurement is taken, and then the patient is made to inhale the medicine. If there is a decrease in lung function with an increased dose of methacholine, the test is positive.
- FeNO Test: The FeNO test, which is the exhaled nitric oxide test, measures the inflammation in your airways.
- Bronchial Provocation or Trigger Tests: These tests measure the sensitivity of the lungs and how they respond to certain irritants, such as chemicals or allergens.
- Peak Flow Meter Tests: This test measures the capacity of your lungs to push out the air. They are less accurate than spirometry but can be used for regular testing at home. Other than the diagnosis, it can also be used to check the efficacy of the treatment.
Allergy Tests
Two major allergy tests for asthma are skin prick and serum-specific IgE tests. The skin prick test uses a small amount of allergen solutions. The solution is applied to the forearm or back, and the skin is pricked using a lancet. If the test is positive, the skin reacts to the allergen and swells, forming a welt. Serum-specific IgE or blood tests detect IgE antibodies in your blood. These antibodies are formed in the body after exposure to allergens like pollen, dust, etc.
Conclusion:
Asthma is a chronic lung disease that causes chest pain, cough, wheezing, and breathlessness. Allergens like dust, molds, pollen grains, and certain chemicals trigger it. Medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests are used to diagnose asthma. The diagnosis is essential to starting the proper treatment with inhalers and tablets according to the severity of the disease. Remember that you can be sure of a successful treatment only when you diagnose the condition timely. So, if you witness any of the symptoms, visit your doctor, get all the tests done, and start the treatment as soon as possible.
Advertisement